Alexander von Humboldt y la unidad de la naturaleza
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18443/260Keywords:
Unidad de la naturaleza, filosofía de la ciencia, historia de la ciencia, vitalismo, geografía de plantasAbstract
Resumen
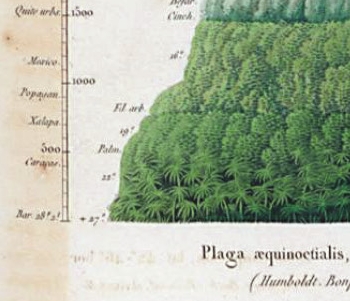
La tesis de esta contribución es que las investigaciones de Alexander von Humboldt ejemplifican un ‘programa de investigación progresivo’ (Imre Lakatos 1978). Examino la propuesta de Adolf Meyer-Abich (1968) de que el método de Humboldt se deriva de un vitalismo inicial y luego desmentido por el científico. Yo propongo, sin embargo, que en realidad es el principio humboldtiano de buscar la unidad en la naturaleza el cual funciona como ‘principio regulativo’, y por consiguiente motiva al investigador a buscar evidencia empírica de relaciones sistémicas entre fenómenos y condicionamientos geográfico-climáticos. Desde este punto de vista es justamente este principio metódico el que empuja a Humboldt a atravesar grandes alturas y latitudes. La visita a Tenerife y al Teide le da una confirmación contundente de la validez de su principio. Concluyo que la influencia de su método en la creación de nuevas ciencias, tales como la biogeografía y la ecología, constituyen razones suficientes para suponer ejemplar el trabajo científico de Humboldt como ‘programa de investigación progresivo’.
Zusammenfassung
Die These dieses Beitrags ist, dass die Forschungsarbeit Alexander von Humboldts ein Beispiel eines ‚progressiven Forschungsprogramms‘ (Imre Lakatos 1978) darstellt. Ich untersuche den Vorschlag Adolf Meyer-Abichs (1968), dass die Methode Humboldts sich von einem anfänglichen Vitalismus, den der Wissenschaftler später abstreitet, ableitet. Meiner Ansicht nach funktioniert eher das Humboldt’sche Prinzip der Suche nach der Einheit der Natur als ‚regulatives Prinzip‘, welches den Forscher motiviert, empirische Nachweise der systemischen Beziehungen zwischen Phänomenen und geographisch-klimatischen Bedingungen zu finden. Aus dieser Sicht heraus ist es genau die Anwendung dieses methodischen Prinzips, welches Humboldt dazu bringt, große Höhen und Breiten zu durchqueren. Der Besuch auf Teneriffa und dem Teide bestätigt ihm die Gültigkeit des Prinzips. Ich schließe daraus, dass der Einfluss seiner Methode in der Bildung neuer Wissenschaften, etwa der Biogeographie und der Ökologie, ausreichende Gründe darstellen, Humboldts wissenschaftliche Arbeit beispielhaft als ‚fortschrittliches Forschungsprogramm‘ zu betrachten.
Abstract
The thesis of this contribution is that Alexander von Humboldt's research exemplifies a 'progressive research program' (Imre Lakatos 1978). I examine Adolf Meyer-Abich’s (1968) proposal that Humboldt's method derives from an initial vitalism, which the scientist later denies. I propose, however, that actually it is Humboldt’s principle of the unity of nature, which functions as a 'regulative principle', thereby motivating the researcher to seek empirical evidence of systemic relationships between phenomena and geographic-climatic conditions. Seen from this perspective, it is precisely this methodical principle that pushes Humboldt to traverse great heights and latitudes. His visit to Tenerife and the Teide provides him with a strong confirmation of the validity of the principle. I conclude that the influence of his method in the creation of new sciences, such as biogeography and ecology, are sufficient reasons to consider Humboldt's scientific work exemplary of a 'progressive research program'.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2017 Thomas Heyd

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
HiN operates under a Creative Commons-Licence (CC BY-NC 4.0), which permits the reproduction of articles, free of charge, for non-commercial use only and with the appropriate citation information. All authors publishing with HiN accept these terms of publication.
Authors retain the copyright for their articles and reviews. Copyright of the layout and design of HiN articles remains with the journal and cannot be used in other publications.









